Hearing
How we hear
Hearing is our ability to receive sound waves and convert them into sound impressions that our brain can perceive. The ear can be divided into the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear.
Sound waves travel into the ear canal until they reach the eardrum. The eardrum passes the vibrations through the middle ear bones or ossicles into the inner ear. The inner ear is shaped like a snail and is also called the cochlea. Inside the cochlea, there are thousands of tiny hair cells. Hair cells change the vibrations into electrical signals that are sent to the brain through the hearing nerve. The brain tells you that you are hearing a sound and what that sound is.
.
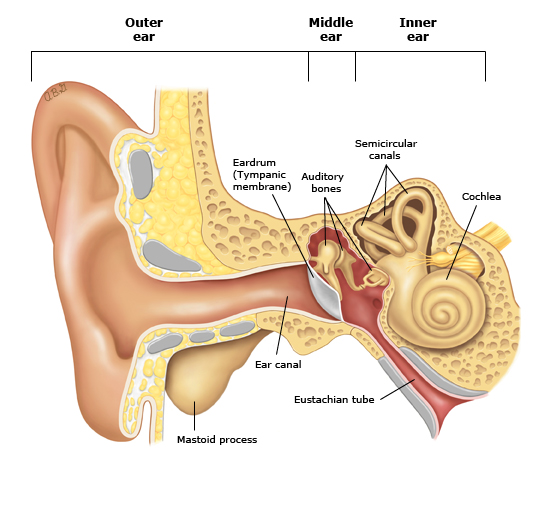
Ear structure
Hearing is the pathway by which sound has access to the brain. Without the ability to hear properly, children cannot learn speech and language adequately, which can in turn have a negative effect on their social, educational, and emotional development
Hearing loss is when your ability to hear is reduced. A hearing loss makes it more difficult for you to hear speech and other sounds. The most common causes of hearing loss are noise and ageing. In most cases a hearing loss cannot be cured.
Each type of hearing loss may have several different causes. Exposure to loud noise is a common cause of both hearing loss and tinnitus. Infections are also a common cause, as are birth defects, genetics and reaction to drugs, especially chemotherapy or drugs used for cancer treatment.
Here are the different causes of each type of hearing loss.
Causes of sensorineural hearing loss:
- Aging
- Injury
- Excessive noise exposure
- Viral infections (such as measles or mumps)
- Shingles
- Ototoxic drugs (medications that damage hearing)
- Meningitis
- Diabetes
- Stroke
- High fever or elevated body temperature
- Ménière’s disease (a disorder of the inner ear that can affect hearing and balance)
- Acoustic tumors
- Heredity
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Hypertension
- Muffling of speech and other sounds.
- Difficulty understanding words, especially against background noise or in a crowd.
- Trouble hearing consonants.
- Frequently asking others to speak more slowly, clearly and loudly.
- Needing to turn up the volume of the television or radio.
Mon - Fri: 9:00 am - 5:00 pm
Sat: 10:00 am - 3:00 pm
hello@ebiishearing.com
info@ebiishearing.com
19, Awolowo Avenue, Bodija, 200212, Ibadan, Nigeria
